The Mr. Rapidan fly pattern was originated by Harry Murray in the 1970’s. Originally tied as a dry fly, it was designed to be a buoyant, visible fly for the choppy waters of Virginia. Does that sound familiar? It should, because much of the trout water in Virginia is very similar to the trout water in Tennessee!
Like many other fly patterns I write about, the Mr. Rapidan has A LOT of branches on its family tree. In fact, if you visit Harry Murray’s online site, you’ll more likely find a description of the Mr. Rapidan family of flies. We’re not going to get into that this time, but you’ll find everything from dry flies to nymphs to ants in the Mr. Rapidan family.
But you’ve surely noticed that the title of this article is not Mr. Rapidan Ant or Mr. Rapidan Family. We are focused on the emerger, mainly because it is time for Quill Gordons to hatch and this is the best pattern for a Quill Gordon emerger I’ve ever used.
The Quill Gordon mayfly is one of the first good hatches of the year in the Smokies. Most folks will tell you it starts coming off around the third or fourth week of March. I wish it was that simple. As an early season hatch, it can be one of the toughest hatches of the year to time right.
Mayflies don’t time their emergence based on a calendar. It usually has more to do with water temperature. When water temperatures get into the 50’s and remain there for the better part of a few days, Quill Gordons will begin to hatch. Usually that’s late March but if we get a warm spell in February, they’ll come off then. If we get a really cold early spring, they may not come off until April. This year, all indications are that they’ll be right on schedule, but it’s still too soon to tell.
During a hatch, some mayfly species spend a fair amount of time on the surface before they fly off. Those are pretty easy picking for trout. However, unless you catch a Quill Gordon hatch on a particularly cool or damp day, they get off the water in a hurry and trout don’t get much of a look at the adults. So the trout often focus their attention more on the emerging insects.
Enter the Mr. Rapidan Emerger. While there are very specific Quill Gordon wet fly patterns, I haven’t found any that outproduce the Mr. Rapidan Emerger. I will sometimes fish it as a dropper below a Quill Gordon dry fly, but most often, I like to fish it by itself or in tandem with another wet fly. Of course, it depends on the specific run but I most often like to fish it on a tight line, “twitching” the rod tip periodically through the drift.
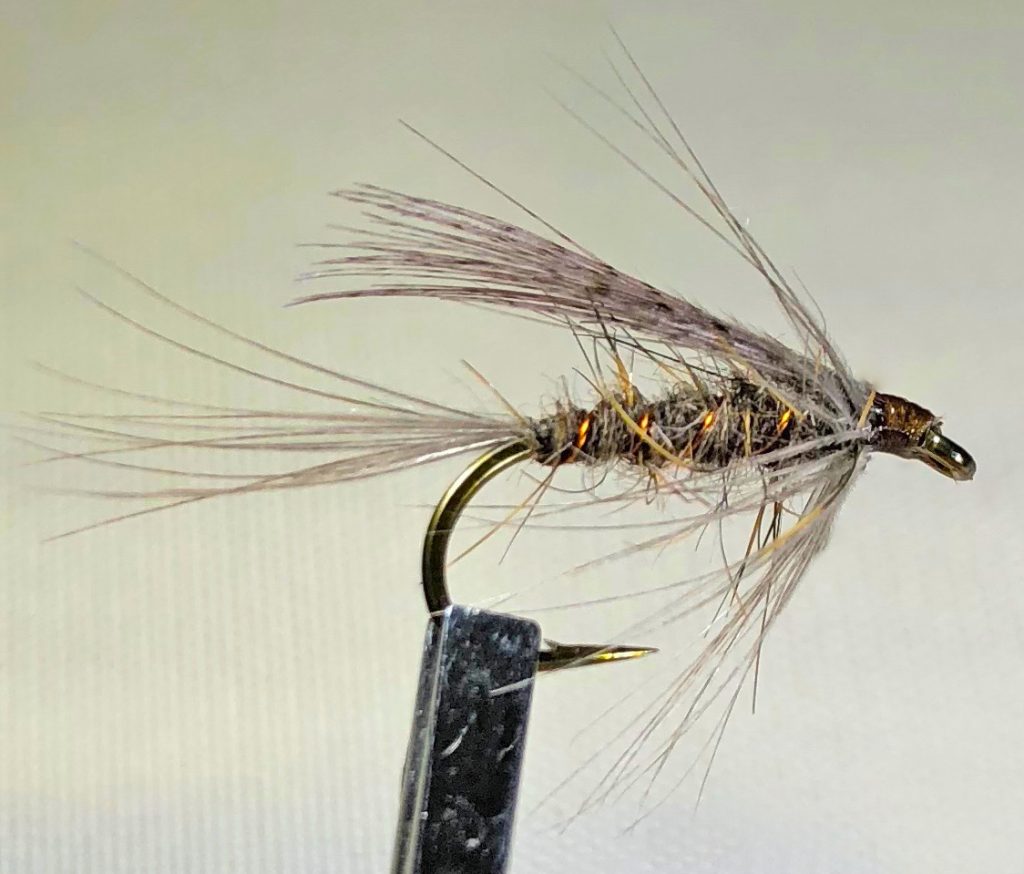
Some variations of this fly have a tail, usually made of pheasant tail fibers. The variation I included does not.
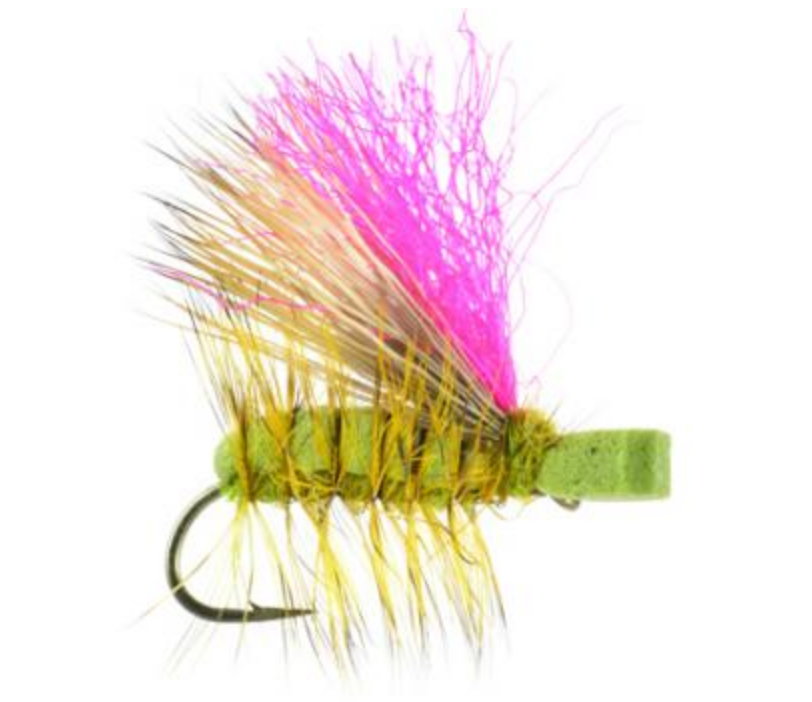
Mr. Rapidan Emerger
Hook: TMC 3769 #14-10
Thread: 8/0 Grey
Rib: Small copper wire
Tail (optional): Pheasant Tail
Body: Dark hare’s ear dubbing
Thorax: Cream antron dubbing
Hackle: Natural hen neck, swept rearward














 Probably 25 years ago, I was fishing the Clinch River with a buddy during the
Probably 25 years ago, I was fishing the Clinch River with a buddy during the 










